1126
General discussions (Q&As) / Re: zero or negative helical rise?
« on: March 25, 2013, 04:20:39 pm »
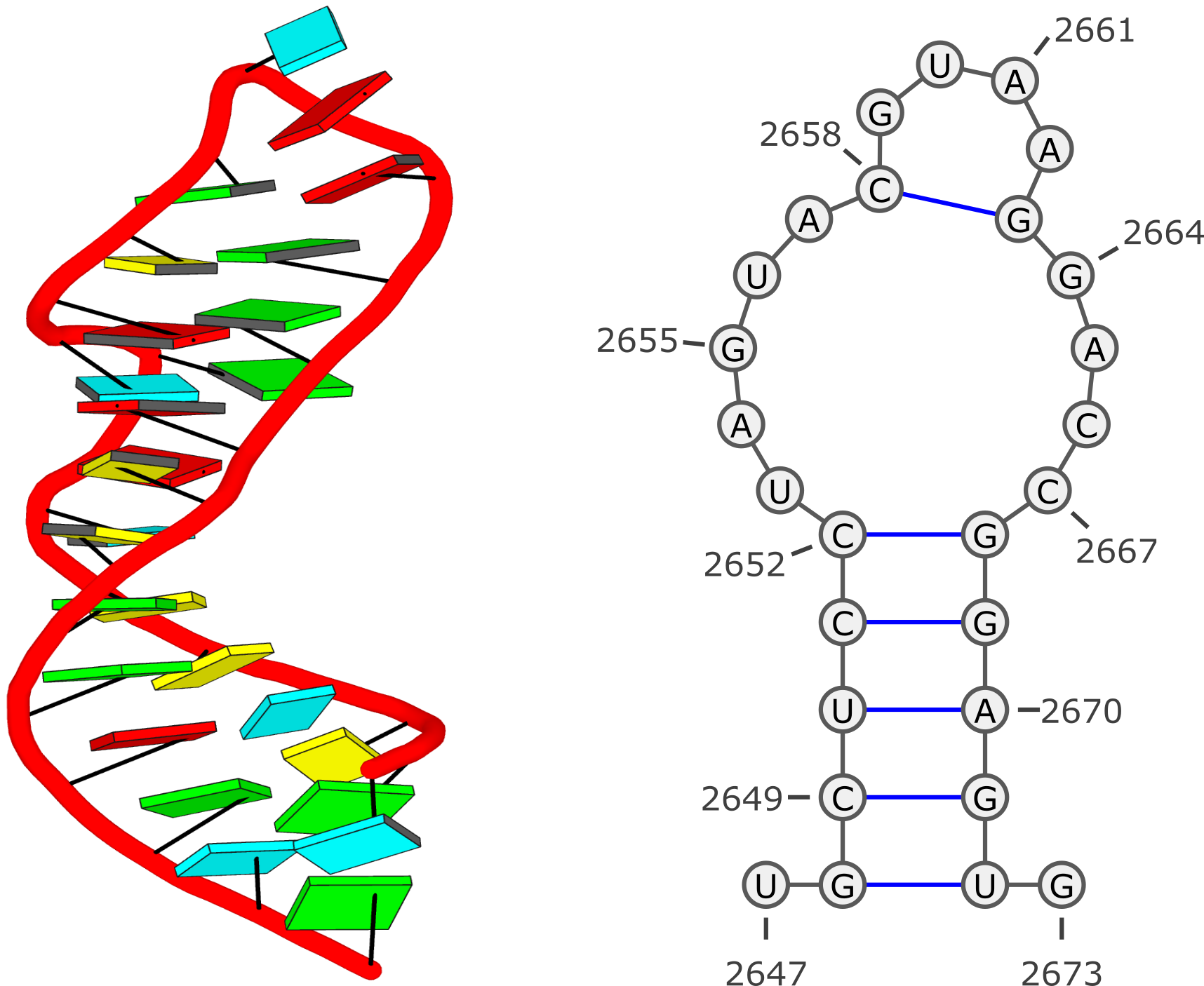
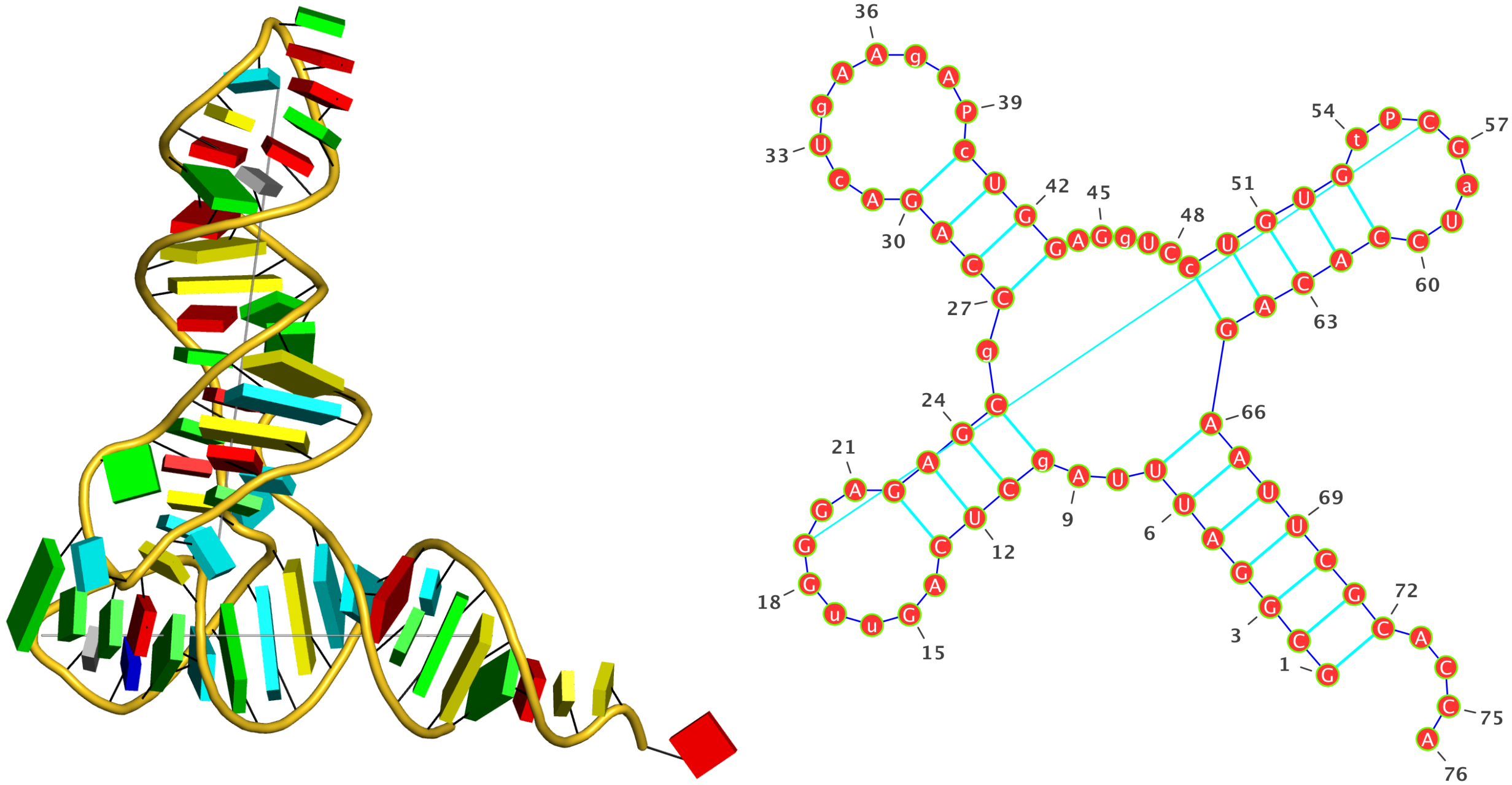
The issue you noticed with negative rise in 1xvk etc is due to the extensive non-canonical base pairs. Under such circumstance, as in more commonly seen in RNA structures, the meaning of base-pair step and helical parameters may not make (much) intuitive sense. Yet, these parameters are required to rigorously characterize the structure. Note that the base-pair parameters (Shear, Stretch, Stagger, Buckle, Propeller and Opening) still have their normal interpretation.
I'd recommend you use DSSR, which shows clearly the two Hoogsteen pairs, among other things, as show below. Check also files dssr-torsions.dat, dssr-pairs.pdb etc.
HTH,
Xiang-Jun
I'd recommend you use DSSR, which shows clearly the two Hoogsteen pairs, among other things, as show below. Check also files dssr-torsions.dat, dssr-pairs.pdb etc.
HTH,
Xiang-Jun
****************************************************************************
DSSR: Software for Defining the (Secondary) Structures of RNA
by Xiang-Jun Lu (xiangjun@x3dna.org), beta-r08-on-20130323
The program is currently under active development. As always, we
greatly appreciate your feedback! Please report all DSSR-related
issues on the 3DNA Forum (http://forum.x3dna.org/), and I strive
to promptly respond to any questions posted there.
****************************************************************************
Date and time: Mon Mar 25 16:15:39 2013
File name: 1xvk.pdb1
no. of DNA/RNA chains: 1 [A=16]
no. of nucleotides: 16
no. of waters: 112
no. of metals: 2 [Mg=2]
****************************************************************************
List of 8 base pair(s)
1 1:A.DG1 2:A.DC8 [G+C] 00-n/a cHW cM+W
74.1(syn) C2'-endo lambda=47.5; -100.4(anti) C2'-endo lambda=61.6
d(C1'-C1')=8.31 d(N1-N9)=6.64 d(C6-C8)=6.16 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=-0.1
H-bonds[2]: "N7*N3[2.69]; O6(carbonyl)-N4(amino)[2.85]"
bp_pars: [0.46 -3.41 -0.35 3.71 -5.92 67.37]
2 1:A.DC2 2:A.DG7 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
-103.9(anti) C4'-exo lambda=55.5; -105.3(anti) C1'-exo lambda=52.5
d(C1'-C1')=10.53 d(N1-N9)=8.80 d(C6-C8)=9.65 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=0.0
H-bonds[3]: "O2(carbonyl)-N2(amino)[2.76]; N3-N1(imino)[2.89]; N4(amino)-O6(carbonyl)[2.74]"
bp_pars: [0.27 -0.18 0.35 -22.28 3.73 -2.75]
3 1:A.DG3 2:A.DC6 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
-108.4(anti) C1'-exo lambda=54.1; -107.8(anti) C4'-exo lambda=54.2
d(C1'-C1')=10.47 d(N1-N9)=8.77 d(C6-C8)=9.65 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=-2.6
H-bonds[3]: "O6(carbonyl)-N4(amino)[2.87]; N1(imino)-N3[2.88]; N2(amino)-O2(carbonyl)[2.81]"
bp_pars: [-0.38 -0.18 0.41 22.84 2.54 -2.67]
4 1:A.DT4 2:A.DA5 [T+A] Hoogsteen 23-XXIII cWH cW+M
-95.4(anti) C2'-endo lambda=59.7; 68.3(syn) C1'-exo lambda=53.5
d(C1'-C1')=8.37 d(N1-N9)=6.77 d(C6-C8)=6.17 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=0.5
H-bonds[2]: "N3(imino)-N7[2.86]; O4(carbonyl)-N6(amino)[2.80]"
bp_pars: [-0.69 3.57 0.31 -3.48 7.41 -70.55]
5 1:A.DA5 2:A.DT4 [A+T] Hoogsteen 23-XXIII cHW cM+W
68.3(syn) C1'-exo lambda=53.5; -95.4(anti) C2'-endo lambda=59.7
d(C1'-C1')=8.37 d(N1-N9)=6.77 d(C6-C8)=6.17 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=0.5
H-bonds[2]: "N7-N3(imino)[2.86]; N6(amino)-O4(carbonyl)[2.80]"
bp_pars: [0.69 -3.57 -0.31 3.48 -7.41 70.54]
6 1:A.DC6 2:A.DG3 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
-107.8(anti) C4'-exo lambda=54.2; -108.3(anti) C1'-exo lambda=54.1
d(C1'-C1')=10.47 d(N1-N9)=8.77 d(C6-C8)=9.65 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=-2.6
H-bonds[3]: "O2(carbonyl)-N2(amino)[2.81]; N3-N1(imino)[2.88]; N4(amino)-O6(carbonyl)[2.87]"
bp_pars: [0.38 -0.18 0.41 -22.84 2.54 -2.67]
7 1:A.DG7 2:A.DC2 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
-105.3(anti) C1'-exo lambda=52.5; -103.9(anti) C4'-exo lambda=55.5
d(C1'-C1')=10.53 d(N1-N9)=8.80 d(C6-C8)=9.65 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=0.0
H-bonds[3]: "O6(carbonyl)-N4(amino)[2.74]; N1(imino)-N3[2.89]; N2(amino)-O2(carbonyl)[2.76]"
bp_pars: [-0.27 -0.18 0.35 22.28 3.73 -2.75]
8 1:A.DC8 2:A.DG1 [C+G] 00-n/a cWH cW+M
-100.4(anti) C2'-endo lambda=61.5; 74.1(syn) C2'-endo lambda=47.6
d(C1'-C1')=8.31 d(N1-N9)=6.64 d(C6-C8)=6.16 tor(N1-C1'-C1'-N9)=-0.1
H-bonds[2]: "N3*N7[2.69]; N4(amino)-O6(carbonyl)[2.86]"
bp_pars: [-0.46 3.41 0.35 -3.71 5.93 -67.37]
****************************************************************************
List of 1 helix
helix=1[2] bps=8
1 1:A.DG1 2:A.DC8 [G+C] 00-n/a cHW cM+W
2 1:A.DC2 2:A.DG7 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
3 1:A.DG3 2:A.DC6 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
4 1:A.DT4 2:A.DA5 [T+A] Hoogsteen 23-XXIII cWH cW+M
5 1:A.DA5 2:A.DT4 [A+T] Hoogsteen 23-XXIII cHW cM+W
6 1:A.DC6 2:A.DG3 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
7 1:A.DG7 2:A.DC2 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
8 1:A.DC8 2:A.DG1 [C+G] 00-n/a cWH cW+M
****************************************************************************
List of 2 stems
stem=1[#1] bps=2
1 1:A.DC2 2:A.DG7 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
2 1:A.DG3 2:A.DC6 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
stem=2[#1] bps=2
1 1:A.DC6 2:A.DG3 [C-G] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
2 1:A.DG7 2:A.DC2 [G-C] WC 19-XIX cWW cW-W
****************************************************************************
List of 1 coaxial stack(s)
1 Helix#1 contains 2 stems: [#1, #2]
****************************************************************************
List of 1 internal loop(s)
1 symmetric internal loop: 8 nts; [2x2]; linked by [#1, #2]
1:A.DG3+1:A.DT4+1:A.DA5+1:A.DC6+2:A.DG3+2:A.DT4+2:A.DA5+2:A.DC6 [GTACGTAC]
****************************************************************************
>chain-A #1 DNA* with 16 nts
GCGTACGCGCGTACGC
.((..((..))..)).